For thousands of years, oils extracted from nuts and seeds have played a crucial role in human nutrition, skincare, and traditional medicine. Among them, peanut oil, also known as groundnut oil, has emerged as a staple cooking oil and natural remedy in many parts of the world. Derived from the seeds of the peanut plant, Arachis hypogaea, this golden-hued oil is prized not only for its distinctive flavor but also for its nutritional richness, high smoke point, and versatile health benefits.
Though best known for its culinary applications, peanut oil’s profile extends far beyond the kitchen. It is packed with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, antioxidants like resveratrol, and skin-beneficial compounds such as vitamin E. Whether used to prepare flavorful stir-fries or to hydrate dry skin, peanut oil is a multifaceted natural resource that blends ancient tradition with modern wellness practices.
In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about peanut oil. its history, extraction methods, chemical composition, health benefits, skincare and haircare uses, cooking applications, precautions, and how to choose the best quality product. So let’s dive into the world of this aromatic, nutty oil and discover why it has become a global favorite.
Origins and Historical Use of Peanut Oil
The peanut plant, though native to South America, has a long and storied journey that spans continents and cultures. Archaeological evidence shows that peanuts were cultivated in Peru and Brazil over 3,500 years ago. Spanish explorers brought them to Europe in the 16th century, and eventually, peanuts spread across Africa and Asia, becoming a dietary staple.
In India and China, peanut oil gained popularity as a cooking oil and was also used in Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine for its warming, nourishing properties. By the early 20th century, peanut oil was industrially processed in the United States, often used not just in kitchens, but also in soapmaking, lubricants, and medicinal ointments.
Today, it remains especially popular in Asian, African, and Southern U.S. cuisines, cherished for its mild nutty taste and exceptional cooking versatility.
Extraction Method How Peanut Oil is Made
There are three primary types of peanut oil based on how it’s processed
Refined Peanut Oil
This is the most common commercial variety. It undergoes bleaching, deodorizing, and refining, which removes allergens and creates a neutral flavor. This oil has a high smoke point~450°F/232°C, making it ideal for high-heat cooking like deep frying.
Cold-Pressed Virgin or Unrefined Peanut Oil
Made by mechanically pressing peanuts without heat, this version retains its natural aroma, flavor, and nutrients. It’s best used for low to medium-heat cooking or as a finishing oil.
Gourmet Roasted Peanut Oil
Made by pressing roasted peanuts, this oil is highly aromatic and flavorful. It’s best used in dressings, marinades, and finishing dishes to impart a rich, nutty essence.
Each variety has unique advantages depending on culinary and therapeutic needs.
Chemical Composition of Peanut Oil
Peanut oil is nutritionally rich, offering a balance of fatty acids and antioxidants that contribute to both health and flavor.
Fatty Acid Breakdown
Monounsaturated fats Oleic acid– 46–50%
Polyunsaturated fats Linoleic acid – 30–35%
Saturated fats Palmitic and Stearic acids 15–20%
Key Nutrients & Compounds
Vitamin E TocopherolsStrong antioxidant, supports skin and heart health
Phytosterols are Plant compounds that help reduce cholesterol absorption
Resveratrol, an Antioxidant also found in red wine, supports cardiovascular and brain health
Squalene A Moisturizing compound with anti-aging benefits
This nutritional makeup makes peanut oil not only a delicious cooking medium but also a protective agent for skin, heart, and metabolism.
Health Benefits of Peanut Oil
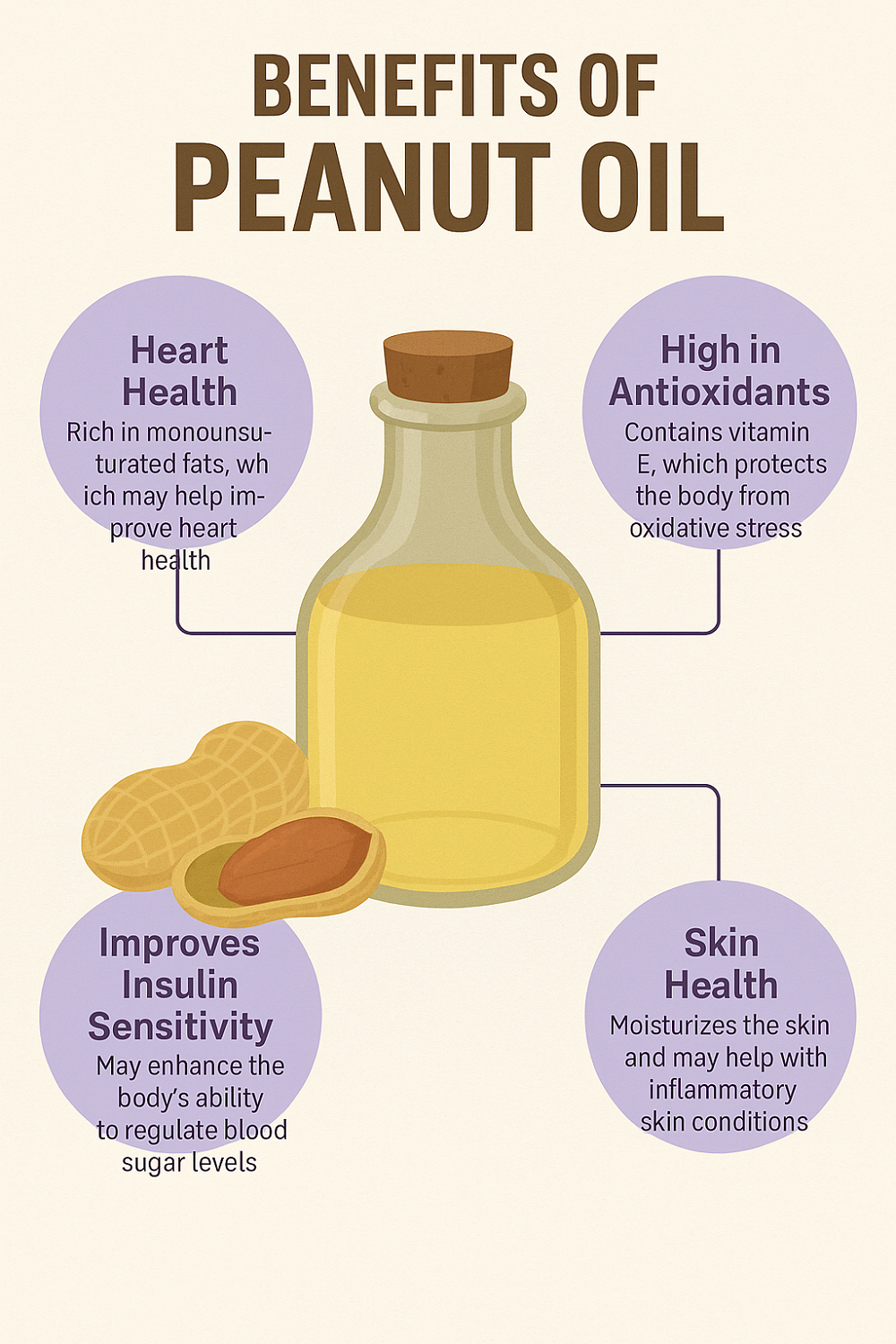
Promotes Heart Health
Thanks to its high content of monounsaturated fats, peanut oil helps lower LDL bad cholesterol levels while raising HDL good cholesterol. The phytosterols and resveratrol in peanut oil add further cardiovascular protection by reducing inflammation and supporting arterial flexibility. When used in moderation as part of a balanced diet, it can help lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Rich in Antioxidants
Peanut oil is an excellent source of vitamin E, a potent antioxidant that helps combat free radical damage, slows cellular aging, and protects against chronic diseases. Additionally, resveratrol provides anti-inflammatory and anti-aging effects while supporting immune and brain health.
Supports Insulin Sensitivity
Some studies suggest that diets rich in monounsaturated fats, such as those found in peanut oil, may improve insulin sensitivity and help manage type 2 diabetes. While more research is needed, replacing saturated fats with healthier oils like peanut oil may have a beneficial effect on blood sugar regulation.
Boosts Cognitive Function
The presence of resveratrol and vitamin E contributes to brain health and cognitive longevity. These compounds reduce oxidative stress and may lower the risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Anti-Cancer Properties
Although more clinical evidence is needed, resveratrol has shown promise in laboratory settings for its anti-cancer properties, including the inhibition of tumor growth and reduction of cancer cell spread. Combined with other antioxidants in peanut oil, it may offer protection against certain types of cancers when consumed as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Peanut Oil for Skin Care
Peanut oil isn’t just a star in the kitchen; it’s also a natural ally in skincare routines. Due to its emollient and anti-inflammatory properties, it can be used to moisturize, heal, and rejuvenate skin.
Deep Hydration and Barrier Protection
Peanut oil is rich in oleic acid and squalene, which penetrate the skin deeply, locking in moisture and reinforcing the skin’s barrier. It’s especially helpful for dry, flaky, or mature skin, leaving it feeling soft and nourished.
Reduces Inflammation and Redness
Thanks to its vitamin E and resveratrol content, peanut oil helps soothe irritated or inflamed skin. It’s useful for mild rashes, sunburn, and eczema. When blended with soothing essential oils like chamomile or lavender, it can become a powerful natural remedy for inflammation.
Fade Scars and Stretch Marks
Regular use of peanut oil can improve skin elasticity and promote cell turnover, helping to fade scars, blemishes, and stretch marks over time. Its antioxidants support collagen production and protect the skin from further damage.
Anti-Aging Benefits
Peanut oil’s vitamin E content helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It neutralizes oxidative stress and helps maintain skin’s elasticity, making it a gentle yet effective anti-aging treatment.
Peanut Oil for Hair Care
While not as common in commercial hair products, peanut oil offers impressive benefits when used directly or in DIY treatments.
Nourishes and Strengthens Hair
Peanut oil coats hair strands with protective moisture, making them more resistant to breakage and split ends. It adds shine and softness without weighing the hair down.
Stimulates Hair Growth
Massaging warm peanut oil into the scalp increases circulation and delivers essential nutrients to hair follicles. This encourages hair growth and strengthens roots, especially when used consistently over time.
Fights Dandruff and Dry Scalp
Its anti-inflammatory and antifungal properties help reduce scalp itchiness, flaking, and irritation, especially in cases of dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis.
Culinary Uses and Cooking Benefits
Peanut oil’s most famous role is in the kitchen, where it shines due to its high smoke point, neutral taste, and nutty aroma.
High Heat Cooking
Refined peanut oil has a smoke point of approximately 450°F 232°C making it ideal for:
Deep frying, e.g., French fries, chicken
Stir-frying is common in Chinese and Thai cuisine.
Grilling and roasting
Its stability at high temperatures reduces the production of harmful free radicals compared to oils that break down quickly.
Flavor Enhancer
Roasted peanut oil imparts a rich, nutty flavor to dishes. A few drops in a salad dressing, noodle dish, or marinade can elevate the taste instantly.
Heart-Healthy Alternative
Using peanut oil instead of butter, margarine, or lard can reduce your intake of saturated fats, aligning with heart-healthy dietary guidelines.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While peanut oil has many benefits, it’s important to be aware of a few potential concerns:
Peanut Allergies
Although refined peanut oil is generally considered safe for those with peanut allergies due to the removal of allergenic proteins, cold-pressed or unrefined versions may contain trace allergens. Always consult an allergist or avoid the oil entirely if you have a known peanut allergy.
Omega-6 Overload
Peanut oil is high in omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential but can cause inflammation when consumed in excess relative to omega-3s. To balance this, ensure you consume enough omega-3-rich foods like flaxseed, walnuts, or fish. alongside peanut oil.
Oxidation Risk
Peanut oil, especially unrefined types, can become rancid quickly when exposed to heat, light, or air. Store in a cool, dark place and use within 6 12 months.
