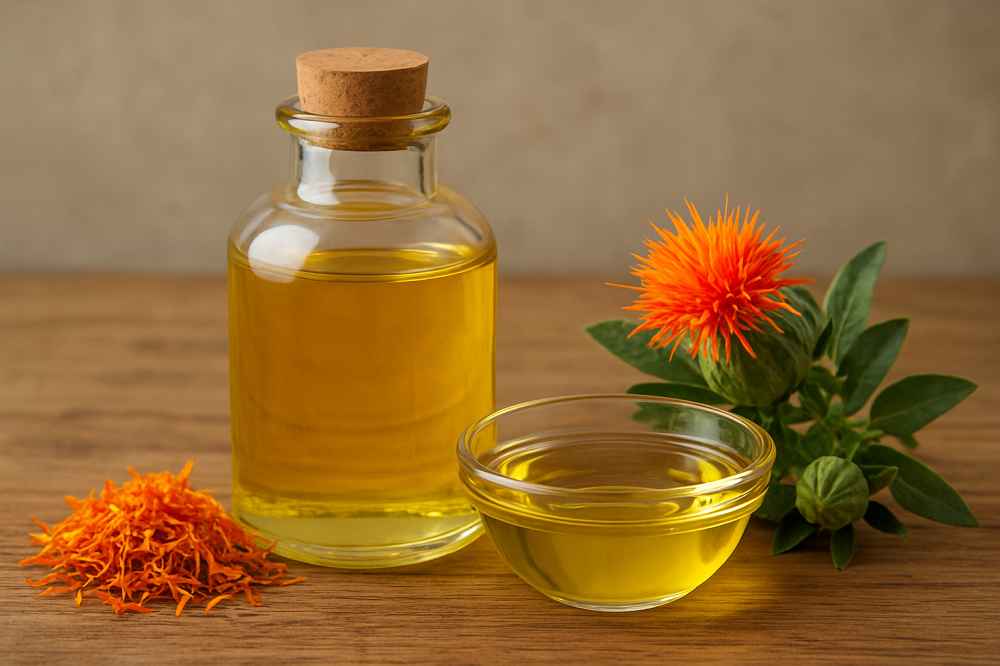
Safflower oil is extracted from the seeds of the safflower plant Carthamus tinctorius. It is one of the lesser-known yet highly beneficial vegetable oils available today. For centuries safflower has been cultivated for its seeds and petals initially used as a dye plant before gaining recognition as a nutritional and medicinal oil source. Unlike other oils that are commonly discussed in both culinary and wellness circles safflower oil remains somewhat underrated even though it contains a rich profile of fatty acids, antioxidants, and essential nutrients.
However this oil has gained popularity due to its association with heart health skin nourishment weight management and even blood sugar control. We will dive deep into the history nutritional composition types health benefits skincare applications and culinary uses of safflower oil providing a complete overview for anyone interested in understanding its role in modern wellness.
A Brief History of Safflower and Its Oil
The safflower plant has a long history that can be traced back over 4000 years with evidence of its cultivation found in ancient Egyptian tombs. Initially safflower was used primarily for its bright red and yellow petals which were employed as natural dyes for fabrics cosmetics and even food coloring. It was only later that people began extracting oil from its seeds recognizing its potential as both a cooking oil and a therapeutic substance.
Traditional systems of medicine particularly in Asia and the Middle East valued safflower oil for its ability to reduce inflammation improve circulation and support women’s reproductive health. As global trade expanded safflower spread across different regions and its oil began to be appreciated for its nutritional richness and cooking versatility. Today safflower is cultivated worldwide with major producers including India the United States Mexico and parts of Africa.
Nutritional Composition of Safflower Oil
Safflower oil is often considered a healthier alternative to many other vegetable oils because of its high content of unsaturated fatty acids especially linoleic and oleic acids. Depending on the variety safflower oil can either be high in polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFA or monounsaturated fatty acids MUFA. This difference makes safflower oil highly versatile suitable for both high-heat cooking and nutritional supplementation.
Calories One tablespoon of safflower oil contains about 120 calories most of which come from healthy fats.
Fatty Acids The oil contains between 70% to 80% unsaturated fatty acids with a focus on linoleic acid an omega-6 fatty acid and oleic acid an omega-9 fatty acid.
Vitamin E Safflower oil is rich in tocopherols a form of vitamin E which acts as a natural antioxidant protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Phytosterols These compounds are known for their cholesterol-lowering properties and are present in notable amounts in safflower oil.
What makes safflower oil unique compared to other cooking oils is its neutral flavor and light texture making it easy to incorporate into various dishes without overpowering other ingredients. Its nutritional composition also contributes significantly to its wide array of health benefits.
Types of Safflower Oil
There are two main types of safflower oil available on the market and the health benefits depend on the variety
High-Linoleic Safflower Oil Polyunsaturated Fat
This variety is high in linoleic acid an omega-6 fatty acid and is especially useful for supporting cardiovascular health. It is typically consumed raw or used in salad dressings dips and low-heat cooking to preserve its delicate structure.
High-Oleic Safflower Oil Monounsaturated Fat
This version contains a higher percentage of oleic acid and is more stable under heat making it suitable for frying sautéing and baking. It has a higher smoke point compared to many other oils making it a favorite for chefs who want a neutral oil with strong performance.
Health Benefits of Safflower Oil
1. Supports Heart Health
One of the most widely researched benefits of safflower oil lies in its ability to promote cardiovascular wellness. The oil’s high unsaturated fat content helps lower levels of LDL cholesterol bad cholesterol while maintaining or increasing HDL cholesterol good cholesterol. This balance reduces the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries thereby lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke. In addition the oil contains compounds that may help reduce blood pressure further supporting overall heart health.
May Help Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Several studies have indicated that safflower oil can play a role in improving blood sugar regulation particularly in people with type 2 diabetes. Its high linoleic acid content helps improve insulin sensitivity allowing glucose to be metabolized more effectively by the body. By incorporating safflower oil into a balanced diet individuals may experience improved glycemic control over time making it a useful addition to diabetic-friendly meal planning.
Supports Weight Management
Interestingly, safflower oil has been studied for its potential effects on weight loss and body fat distribution. Some research suggests that daily consumption of safflower oil may help reduce abdominal fat especially in overweight or obese individuals. While it should not be considered a magic weight-loss solution its metabolism-boosting fatty acids may play a role in supporting healthier body composition when combined with exercise and a balanced diet.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is at the root of many modern health problems, including heart disease, arthritis, and even certain cancers. Safflower oil contains anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce markers of inflammation in the body. This makes it particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from inflammatory conditions such as joint pain or skin irritation.
Boosts Skin Health
Thanks to its high vitamin E content and fatty acid profile safflower oil is widely used in skincare. It moisturizes deeply without clogging pores making it suitable for individuals with acne-prone or sensitive skin. Vitamin E also provides antioxidant protection reducing the effects of free radicals that contribute to premature aging. Safflower oil may also help reduce eczema symptoms and support overall skin elasticity.
Improves Hair Quality
Safflower oil has been incorporated into hair care routines due to its ability to nourish hair follicles improve scalp circulation and strengthen strands. Its fatty acids lock in moisture reducing dryness and brittleness while promoting shine. Some people even massage safflower oil directly into their scalp to support healthier hair growth and combat dandruff.
Supports Immune Function
The antioxidants in safflower oil particularly vitamin E, strengthen the immune system by protecting cells from damage. Additionally the oil’s fatty acids contribute to overall cellular health, supporting the body’s ability to fight infections and recover from illness.
Skincare and Cosmetic Uses of Safflower Oil
Beyond its role in cooking safflower oil is a valuable ingredient in the beauty industry. Its lightweight texture and non-comedogenic properties make it a popular choice for natural moisturizers facial serums and body oils. Unlike heavier oils safflower oil absorbs quickly into the skin leaving it soft and supple without feeling greasy. It can also be blended with essential oils like lavender tea tree or rosehip oil to create customized skincare remedies.
For those struggling with acne safflower oil provides hydration without clogging pores helping to maintain the skin’s natural balance. Its anti-inflammatory properties also soothe redness and irritation making it a gentle yet effective option for sensitive skin types. Additionally safflower oil can be used as a natural makeup remover dissolving foundation and mascara while nourishing the skin at the same time.
Culinary Uses of Safflower Oil
One of safflower oil’s biggest advantages is its versatility in the kitchen. Its mild flavor allows it to be used in both sweet and savory dishes without altering the overall taste profile. The high-oleic variety with its stability at high temperatures is especially useful for frying roasting and sautéing.
Salad Dressings High-linoleic safflower oil can be used in vinaigrettes and salad dressings where its delicate flavor enhances fresh vegetables without overpowering them.
Cooking Oil The high-oleic type is an excellent choice for frying or stir-frying due to its high smoke point.
Baking: Safflower oil can be used in cakes muffins and bread recipes as a substitute for butter or margarine providing a healthier fat source.
Marinades and Sauces It works well as a base for marinades adding richness to meats, poultry and seafood.
How to Choose and Store Safflower Oil
When buying safflower oil always look for labels that indicate whether the oil is high-linoleic or high-oleic so you can choose the variety that best suits your needs. Cold-pressed or expeller-pressed oils are preferable as they retain more nutrients compared to refined versions. For skincare purposes organic safflower oil without added chemicals or preservatives is recommended.
To maintain freshness safflower oil should be stored in a cool dark place away from direct sunlight and heat. Once opened it is best to use the oil within six months to a year to prevent oxidation. Refrigeration may also extend its shelf life particularly for high-linoleic varieties that are more sensitive to heat and light.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
While safflower oil is generally safe for most people moderation is key. Because it is rich in omega-6 fatty acids excessive consumption without balancing with omega-3s may contribute to inflammation. For individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications safflower oil may increase the risk of bleeding due to its effects on blood clotting. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare professional before using safflower oil as a supplement.
