When it comes to versatile and health-supportive oils sesame oil has held a prominent place in human history for thousands of years. Often referred to as the queen of oils sesame oil has been used across Asia the Middle East, and parts of Africa not only as a flavorful cooking medium but also as a therapeutic agent in traditional medicine. Extracted from the seeds of the Sesamum indicum plant this golden-yellow or sometimes dark-brown oil has been prized for its unique taste, high smoke point and impressive nutritional content.
Sesame oil has grown in popularity in Western wellness circles as more people discover its richness in antioxidants anti-inflammatory compounds and skin-nourishing properties. This blog post will explore sesame oil in great detail from its history and nutritional profile to its health benefits culinary applications and role in skincare and medicine providing a comprehensive resource for anyone looking to incorporate this ancient oil into their modern lifestyle.
The History and Cultural Significance of Sesame Oil
Sesame oil’s roots trace back thousands of years, with evidence suggesting that sesame seeds were cultivated in the Indus Valley Civilization as early as 3,000 BCE. Ancient cultures such as Mesopotamia Egypt and China valued sesame oil for its long shelf life medicinal qualities and spiritual symbolism. Sesame was one of the first oilseed crops known to humanity, which makes its role in human development deeply significant.
The phrase open sesame made famous by the tale of Ali Baba and the Forty Thieves hints at the magical allure and high regard that sesame seeds once held. In Ayurveda the traditional system of Indian medicine sesame oil is considered a sacred healing substance often used for massage detoxification and as a carrier for herbal preparations. Similarly in Chinese medicine sesame oil was applied for its ability to balance yin and yang energy while promoting overall vitality. Beyond healing traditions sesame oil also played an important role in religious rituals cooking and even as a lamp fuel in ancient temples symbolizing its multipurpose nature.
Nutritional Profile of Sesame Oil
One of the key reasons sesame oil is considered such a powerful health food lies in its nutrient composition. Cold-pressed sesame oil is particularly valued because it retains the highest amount of beneficial compounds. The oil is rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids which are heart-friendly and support overall cardiovascular health.
Specifically sesame oil typically contains around 40% oleic acid a monounsaturated fat and 40% linoleic acid a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid alongside smaller amounts of stearic and palmitic acids. It also contains unique antioxidants such as sesamol sesamin and sesamolin which are rare compounds not commonly found in other edible oils. These compounds help protect the oil from oxidation giving it a long shelf life and making it a stable choice for cooking. Sesame oil also contains vitamin E B-complex vitamins and trace minerals like calcium magnesium copper and zinc all of which contribute to its diverse health benefits.
Health Benefits of Sesame Oil
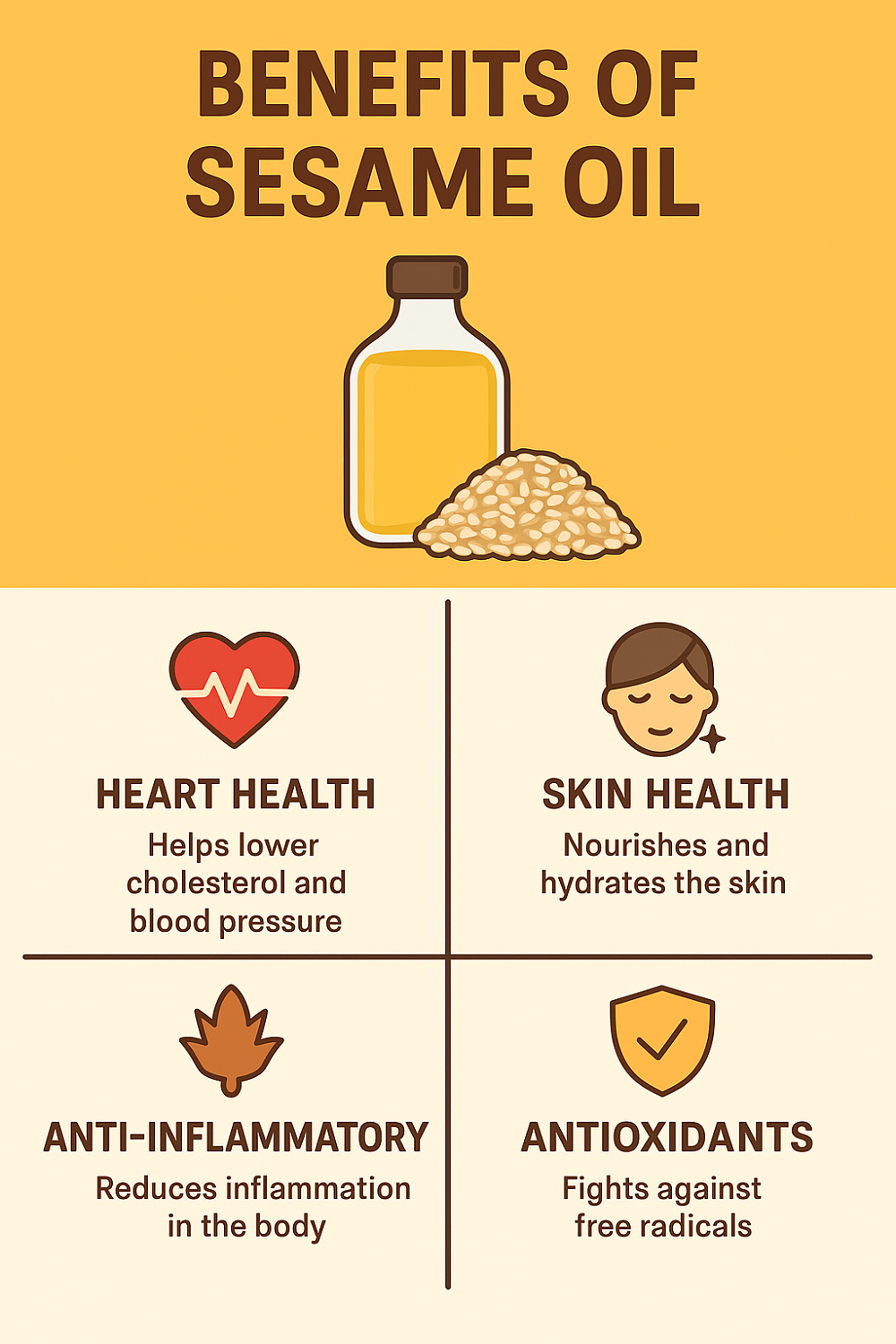
Heart Health and Cholesterol Regulation
Sesame oil is a heart-friendly oil due to its balance of healthy fats and antioxidants. The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats it contains help reduce LDL cholesterol the bad cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol the good cholesterol. Studies have shown that regular consumption of sesame oil may lower blood pressure and improve vascular health making it a supportive dietary addition for individuals with hypertension or those looking to prevent cardiovascular diseases. The antioxidants particularly sesamol and vitamin E help protect blood vessels from oxidative damage further reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Rich Source of Antioxidants
Sesame oil is unique among edible oils for its powerful antioxidant properties. Compounds like sesamol and sesamolin neutralize free radicals in the body which are harmful molecules linked to aging inflammation and chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. These antioxidants are heat-stable, meaning sesame oil retains much of its health-protecting capacity even when used in cooking, unlike some other oils that degrade at high temperatures.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many modern health problems including arthritis metabolic syndrome and even Alzheimer’s disease. Sesame oil’s natural anti-inflammatory compounds help reduce inflammation in tissues and joints. Ayurvedic practitioners have long utilized sesame oil for oil pulling and massage therapies due to its ability to soothe inflammation, relieve pain, and support joint mobility.
Skin and Hair Health
Sesame oil is a natural emollient making it one of the most widely used oils in skincare and haircare. When applied topically it hydrates dry skin improves elasticity and provides a protective barrier against UV damage and environmental pollutants. Its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties make it effective in treating conditions like eczema psoriasis and acne. In hair care sesame oil nourishes the scalp strengthens follicles and reduces dandruff. It has even been traditionally used as a natural sunscreen and a remedy for premature hair graying.
Supports Oral Health Oil Pulling
One of the most well-known Ayurvedic practices involving sesame oil is oil pulling a method where the oil is swished around the mouth for 10–20 minutes. This practice is believed to detoxify the body reduce harmful oral bacteria, prevent gum disease and improve overall dental hygiene. Studies support that oil pulling with sesame oil can reduce plaque formation and gingivitis making it an effective natural alternative to commercial mouthwashes.
Bone Health and Hormonal Support
Sesame oil contains trace minerals such as calcium zinc and copper all of which are essential for bone density and strength. Regular consumption may help prevent osteoporosis and improve skeletal health. Additionally the phytoestrogens in sesame oil may support hormonal balance particularly in women going through menopause by alleviating symptoms such as hot flashes and bone loss associated with estrogen decline.
Digestive and Metabolic Benefits
Sesame oil has a mild laxative effect and can support digestive health by lubricating the intestines and improving bowel movements. It also promotes better nutrient absorption particularly of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E and K. Furthermore its beneficial fatty acids can improve insulin sensitivity potentially reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Culinary Uses of Sesame Oil
Sesame oil is not just a health tonic; it’s also a culinary delight. Its rich, nutty flavor adds depth and aroma to a variety of dishes. There are generally two types of sesame oil used in cooking: light sesame oil which is made from raw seeds and has a mild flavor suitable for sautéing and frying and toasted sesame oil which has a strong nutty taste and is used as a finishing oil for flavor enhancement.
In Asian cuisine sesame oil is a staple ingredient used in stir-fries marinades dipping sauces noodle dishes and soups. A drizzle of toasted sesame oil can transform simple vegetables rice or salads into fragrant flavorful meals. Because of its high smoke point, light sesame oil is excellent for deep frying, while the darker variety is best reserved for flavoring after cooking.
Sesame Oil in Skincare and Beauty
The cosmetic applications of sesame oil are almost as vast as its culinary uses. People have used it as a moisturizer massage oil, and natural sunscreen. It penetrates the skin easily delivering nutrients deep into the dermis and leaving behind a soft glowing complexion. Its antibacterial and anti-fungal properties also make it an effective natural remedy for wounds burns and fungal infections. Mixed with essential oils, sesame oil acts as an excellent carrier oil for aromatherapy and massage blends. In haircare warm sesame oil is often massaged into the scalp to encourage blood circulation prevent dryness and protect hair from UV damage.
The Role of Sesame Oil in Traditional Medicine
Sesame oil is considered one of the most important oils for holistic healing. Known as til taila in Sanskrit it is believed to balance Vata dosha and promote overall health and longevity. It is used in practices like Abhyanga full-body oil massage Nasya nasal administration and oil pulling. Traditional Chinese medicine also incorporates sesame oil for nourishing the liver and kidneys improving circulation and supporting longevity. Modern research has confirmed many of these benefits bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and scientific validation.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While sesame oil is generally safe for most people some individuals may experience allergies especially those with sesame seed sensitivity. Sesame allergies are increasingly recognized and can cause mild to severe reactions. Additionally because sesame oil is calorie-dense excessive consumption can contribute to unwanted weight gain. People taking anticoagulant medications should also use sesame oil with caution as its vitamin E content may have mild blood-thinning effects. Moderation and proper medical guidance are always advisable when adding new oils to your health regimen.
