Sunflower oil is a staple in kitchens and skincare routines across the globe, but its value stretches far beyond its wide availability and affordability. Derived from the seeds of the sunflower plant Helianthus annuus, this oil has been used for centuries, evolving from a simple cooking ingredient into a powerhouse of wellness and nutrition. With its mild flavor, high smoke point, and an array of nutritional benefits, sunflower oil fits effortlessly into a healthy lifestyle.
Beyond the kitchen, its soothing, anti-inflammatory properties make it a preferred base in natural skincare and haircare formulations. As consumers grow more health-conscious and environmentally aware, the demand for multi-use, plant-based oils like sunflower oil continues to rise. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about sunflower oil, from its origins and nutritional profile to its culinary versatility and holistic health benefits.
A Rich Historical Legacy and Worldwide Appeal
The cultivation and use of sunflowers date back to 3000 BC, when Native American tribes harnessed the plant for its seeds, oil, and medicinal properties. These early cultures recognized the value of sunflowers not only for sustenance but also for spiritual and ceremonial uses. When Spanish explorers brought sunflower seeds back to Europe in the 16th century, the plant quickly gained popularity for its hardiness and utility.
Today, sunflower oil is one of the most produced vegetable oils globally, with major contributions from countries like Ukraine, Russia, Argentina, and the United States. Its widespread popularity can be attributed to its low cost, light taste, and exceptional health benefits. Whether used in home cooking, commercial food production, or personal care products, sunflower oil continues to hold a crucial place in both traditional and modern applications.
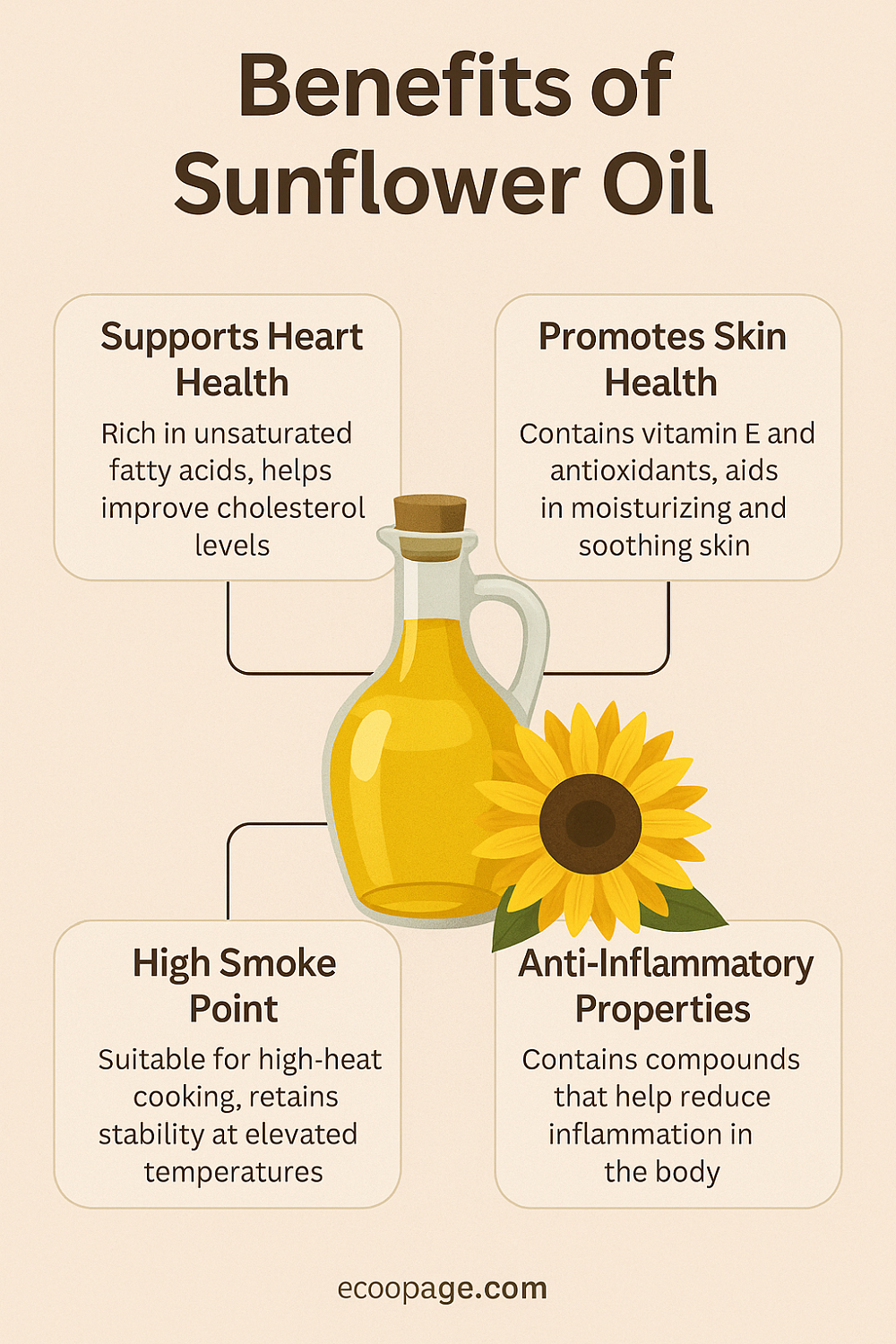
Nutritional Composition Why Sunflower Oil Is Good for You
Sunflower oil is often celebrated for its impressive nutritional content, particularly its healthy fat profile. The oil is rich in unsaturated fats, including linoleic acid omega-6, and oleic acid omega-9, both of which are essential for various bodily functions. The composition of sunflower oil can vary depending on the type of seed and processing method used. Most commercially available sunflower oils fall into one of several categories: high linoleic, high oleic, mid-oleic, and NuSun.
Each has a different balance of fatty acids and is suited for specific culinary or health needs. In addition to healthy fats, sunflower oil contains notable levels of vitamin E tocopherols, which serve as potent antioxidants. These compounds help neutralize free radicals in the body, supporting cellular health, skin integrity, and immune function. Phytosterols in sunflower oil contribute to cardiovascular wellness by reducing cholesterol absorption in the intestines. Moreover, compounds like squalene and choline offer anti-aging and cognitive support, making this oil a well-rounded addition to both diet and skincare.
Sunflower Oil and Cardiovascular Health
Heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, and dietary fats play a significant role in managing cardiovascular risk. Fortunately, sunflower, especially the high oleic variant, is rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been proven to support heart health. When consumed as a replacement for saturated fats or trans fats, monounsaturated fats can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, raise HDL (good) cholesterol, and reduce blood pressure.
The vitamin E content in sunflower oil provides additional cardiovascular protection by preventing oxidative damage to lipoproteins. This prevents the formation of plaques in arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. A balanced intake of sunflower oil, alongside a fiber-rich, plant-forward diet, can help improve lipid profiles, support endothelial function, and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Moreover, the oil’s light, neutral flavor makes it easy to incorporate into everyday cooking without altering the taste of meals, allowing users to gain health benefits without sacrificing culinary enjoyment.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Immune Support
Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many degenerative diseases, including arthritis, diabetes, and even cancer. Sunflower oil can help counteract these issues, especially when consumed in moderation and balanced with omega-3 intake. The omega-6 fatty acids found in sunflower oil, while essential, can contribute to inflammation if consumed excessively. However, balanced omega-6 intake, in the context of a diet also rich in omega-3s, supports immune responses and cellular communication.
The vitamin E and phytosterols in sunflower oil have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects, helping to regulate immune activity and mitigate oxidative stress. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals, which otherwise damage cells and contribute to inflammation. This means sunflower oil not only benefits your immune system on a foundational level but may also offer relief from inflammatory conditions like asthma, arthritis, and skin issues. By integrating high-quality sunflower oil into your meals and skincare routines, you can harness its soothing, immunity-enhancing properties for comprehensive wellness.
Deep Moisturizing and Skin Repair Benefits
When it comes to skin health, sunflower oil is one of the most effective and gentle moisturizers available in the natural skincare world. It contains high amounts of linoleic acid, an essential fatty acid that strengthens the skin barrier, retains moisture, and promotes softness. For people with dry, flaky, or irritated skin, sunflower oil offers instant relief by improving the skin’s ability to hold water. Moreover, the vitamin E in the oil protects against UV damage and environmental pollutants, reducing premature aging and pigmentation.
Sunflower oil is also suitable for sensitive skin, including that of babies. Research published in Pediatric Dermatology showed that applying sunflower oil to premature infants improved skin barrier function significantly, reducing infection risks and skin damage. Whether used as a standalone facial oil, mixed into lotions, or applied as a post-bath body oil, sunflower oil delivers deep nourishment without clogging pores or leaving behind a greasy residue. It’s a natural, affordable, and effective solution for maintaining youthful, radiant skin.
Haircare Power From Scalp to Split Ends
Sunflower oil isn’t just great for your skinit’s also a boon for your hair and scalp. Rich in fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin E, this oil works as an excellent conditioner and treatment for various hair concerns. It moisturizes the scalp, reducing dryness and flakiness while improving blood circulation, which can potentially support hair growth. The antioxidant properties of vitamin E also help fight damage caused by pollution, sun exposure, and heat styling.
For brittle and damaged hair, sunflower oil smooths the cuticle layer, reducing frizz and adding shine. Regular use can prevent split ends, minimize hair breakage, and restore lost elasticity to chemically treated hair. It’s also lightweight, meaning it won’t weigh down your strands or cause buildup. Whether used as a hot oil treatment, scalp massage oil, or serum for the ends, sunflower oil helps promote thicker, shinier, and healthier hair with minimal effort.
Culinary Uses Versatility and High Heat Stability
In the kitchen, sunflower oil stands out as a versatile and heat-stable cooking oil suitable for a variety of culinary methods. One of its standout features is its high smoke point, which can reach up to 450°F (232°C) in refined varieties. This makes it ideal for deep frying, sautéing, roasting, and grilling, where oils with lower smoke points would oxidize and degrade. Unlike stronger-tasting oils like olive or coconut oil, sunflower oil has a neutral flavor that won’t overpower the natural taste of your ingredients.
This makes it perfect for baking, salad dressings, marinades, and even homemade mayonnaise. Furthermore, its light texture makes it ideal for people seeking an oil that doesn’t leave a greasy mouthfeel. The high oleic versions are more resistant to oxidation, offering a longer shelf life and enhanced nutritional value. For those aiming to cut out trans fats or heavily processed oils, sunflower oil is an excellent alternative that offers performance, health, and taste all in one.
A Natural Base in Aromatherapy and Herbal Medicine
Beyond culinary and cosmetic applications, sunflower oil is also widely used in aromatherapy and traditional medicine as a carrier oil. Thanks to its lightweight, non-comedogenic nature and rich vitamin content, it easily blends with essential oils like lavender, peppermint, eucalyptus, or tea tree to deliver therapeutic benefits. In Ayurveda and naturopathy, sunflower oil is valued for its calming, anti-inflammatory properties and is often used in massage therapy to relieve joint pain, muscle soreness, and stress.
Additionally, it’s used in a practice called oil pulling, where a tablespoon of oil is swished around in the mouth for 10-15 minutes to detoxify the gums, whiten teeth, and support oral hygiene. Sunflower oil also plays a role in topical herbal salves and ointments for wounds, burns, or insect bites due to its natural healing compounds. Its multipurpose nature makes it a must-have in any holistic medicine cabinet.
How to Choose and Store Sunflower Oil
To maximize the benefits of sunflower oil, it’s crucial to select the right type for your needs. Cold-pressed or unrefined sunflower oil is the best choice for skincare and low-heat culinary uses as it retains most of its natural nutrients. For high-heat cooking, opt for refined high-oleic sunflower oil, which offers a longer shelf life and better temperature stability.
Look for organic, non-GMO labels to ensure quality. Always store your sunflower oil in a cool, dark place, preferably in a tinted glass bottle that limits exposure to light and oxygen. This helps preserve its vitamin E content and prevents rancidity. Once opened, it’s best to use the oil within 6–12 months and keep it tightly sealed between uses.
Precautions and Side Notes
While sunflower oil is safe for most people, there are a few precautions to keep in mind. Those with seed allergies should consult a healthcare professional before use. Overconsumption of omega-6-rich oils without a balance of omega-3s can contribute to inflammation, so moderation is key. Choose high oleic varieties when possible to reduce omega-6 intake and emphasize whole-food-based sources of omega-3s like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and fatty fish. Lastly, always patch-test when using sunflower oil topically, especially if you have sensitive or allergy-prone skin.
